Have you ever wanted to change the default commit message in Git config?
In this Git config tutorial you will learn:
- where to find the Git config files
- how to create a custom commit message
- how to use Git alias
If you are completely new to Git checkout out the Git Tutorial for Beginners or my complete Git tutorials playlist on Youtube.
Where do you find the Git config files?
The following Git config files locations are Mac specific.
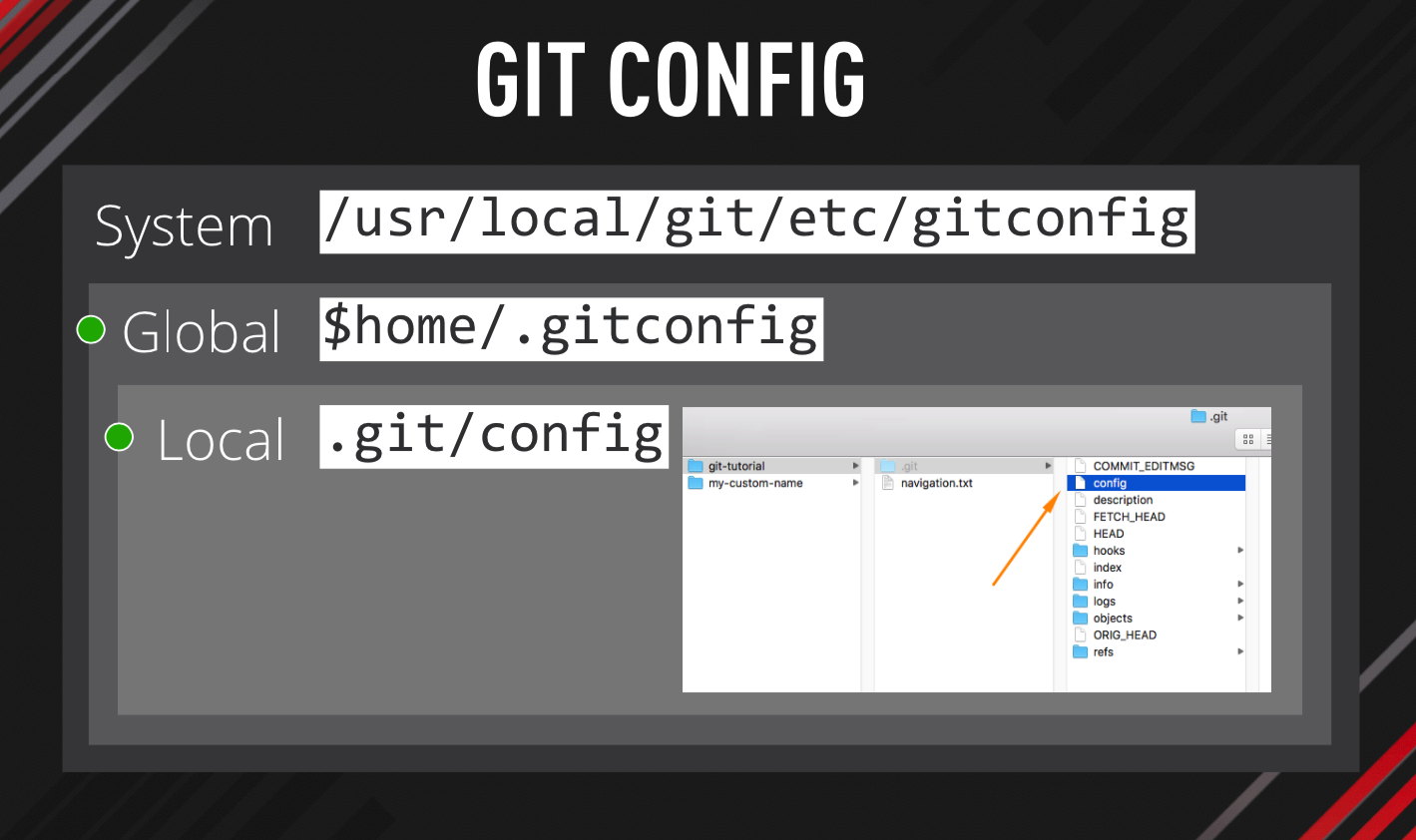
System vs Global vs Local Git config
Before we get to the locations, I just want to clarify that there are 3 different scopes for Git config.
System Git config controls settings for all users and all repositories on your computer.
Global Git config controls settings for the currently logged in user and all his repositories.
Local Git config controls settings for a specific repository.
These 3 config files are executed in a cascading order. First the system, then global and finally the local.
That means that your local Git config will always overwrite settings set in the Global or System configs.
// System /usr/local/git/etc // Global $home/.gitconfig // Local .git/config
In general you most likely want to edit the Global settings and occasionally set some more specific configuration for a single repositories.
Your username and email should be the same for all your repos, that is why it is stored in the Global config.
How do you view your Git config settings?
git config --list git config --list --system git config --list --global git config --list --local
If you don’t specify which of the configs you would like to see, you will get all 3 configs merged into the output in your console.
To edit any of the files use the --edit flag or open the file in a text editor.
How to add or delete a record from Git config?
The following commands would add or remove your name and email from the Global config.
// to add git config --global user.name "Your Name" git config --global user.email "[email protected]" // to remove git config --global --unset user.name git config --global --unset user.email
If you want to read a specific record from Git config use: git config user.name.
How to create a custom Git commit message?
Sometimes it is useful to create a template for your commit messages. This keeps your commits consistent.
To create custom Git commit message firstly create a text file containing your message.
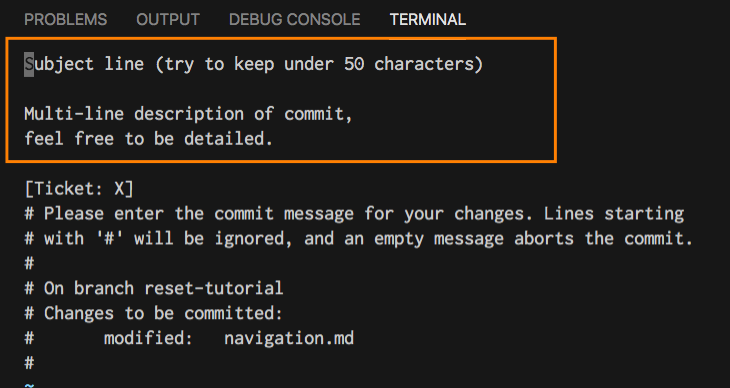
// example from the official Git documentation Subject line (try to keep under 50 characters) Multi-line description of commit, feel free to be detailed. [Ticket: X]
Save this file as .gitmessage in your user directory eg. ~/.gitmessage.
Then update the global config to point to the right location.
git config --global commit.template ~/.gitmessage.txt
Now you should see your own custom message when you make a new commit.
How to use Git alias?
Git alias is another setting saved in the Git config file. It lets you execute longer Git commands by predefined shortcut.
git config --global alias.last "log -1 HEAD"
If you add the above alias to your Git config you can use git last to access the log of your last commit.
The possibilities are endless.
Have you enjoyed this Git tutorial? You might also like
Conclusion
There is much more to Git config, but hopefully this article made it clear how you can configure your own Git environment.
Let me know in the comments what are your own Git tips and tricks.